Standard units
Standard units
Ampere Unit of electric current, the constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length of negligible circular cross-section and placed one metre apart in a vacuum. will produce between them a force equal to 2 x w-7 newton per metre length.
Ampere-hour Unit of quantity of electricity equal to 3.600 coulombs. One unit is represented by one ampere flowing for one hour.
Candela Unit of luminous intensity. It is the luminous intensity, in the perpendicular direction, of a surface of 1/600,000 m- 2 of a full radiator at the temperature of freezing platinum under a pressure of 101.325 newtons m-2
Coulomb Unit of electric charge, the quantity of electricity transported in one second by one ampere.
Decibel (dB) Unit of acoustical or electrical power ratio. Although the bel is officially the unit, this is usually regarded as being too large, so the decibel is preferred. The difference between two power levels, P 1 and P2 , is given as
Farad Unit of electric capacitance. The capacitance of a capacitor between the plates of which there appears a difference of potential of one volt when it is charged by one coulomb of electricity.
Practical units are the microfarad ( w-• farad), the nanofarad (10-9) and the picofarad (10- 12 farad).
Henry Unit of electrical inductance. The inductance of a closed circuit in which an electromotive force of one volt is produced when the electric current in the circuit varies uniformly at the rate of one ampere per second. Practical units arc the microhenry (lo-• henry) and the millihenry ( 10·3 henry).
Hertz Unit of frequency. The number of repetitions of a regular occurrence in one second.
Joule Unit of energy. including work and quantity of heat. The work done when the point of application of a force of one newton is displaced through a distance of one metre in the direction of the force.
Kilovolt-ampere 1.000 volt-amperes.
Kilowatt 1.000 watts.
Lumen m·2 , lux Unit of illuminance of a surface. Mho Unit of conductance. see Siemens.
Newton Unit of force. That force which. applied to a mass of one kilogram. gives it an acceleration of one metre per second per second.
Ohm Unit of electric resistance. The resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant difference of potential of one volt, applied between these two points. produces in the conductor a current of one ampere.
Pascal Unit of sound pressure. Pressure is usually quoted as the root mean square pressure for a pure sinusoidal wave.
Siemens Unit of conductance, the reciprocal of the ohm. A body having a resistance of 4 ohms would have a conductance of 0·25 siemens.
Tesla Unit of magnetic flux density, equal to one weber per square metre of circuit area.
Volt Unit of electric potential. The difference of electric potential between two points of a conducting wire carrying a constant current of one ampere. when the power dissipated between these points is equal to one watt.
Volt-ampere The product of the root-mean-square volts and root-mean-square amperes.
Watt Unit of power, equal to one joule per second. Volts times amperes equals watts.
Weber Unit of magnetic flux. The magnetic flux which, linking a circuit of one turn, produces in it an electromotive force of one volt as it is reduced to zero at a uniform rate in one second.
Light, velocity of Light waves travel at 300,000 kilometres per second (approximately). Also the velocity of radio waves.
Sound, velocity of Sound waves travel at 332 metres per second in air (approximately) at sea level.
Decimal multipliers
Useful formulae
Capacitance
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor can be found from
Cis in picofarads, K is the dielectric constant (air = I), A is the area of the plate in square em and d the thickness of the dielectric.
Calculation of overall capacitance with:
where K =dielectric constant, d.= outside diameter of inner conductor, d,= inside diameter of outer conductor.
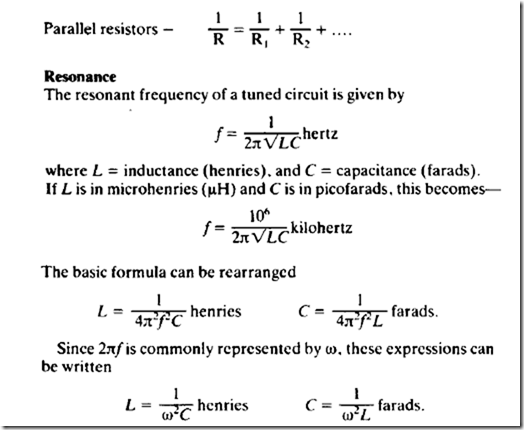
Dynamic resistance
In a parallel-tuned circuit at resonance the dynamic resistance is
where L = inductance (henries), C =capacitance (farads), r = effective series resistance (ohms), Q = Q-value of coil, and w = 2rr x frequency (hertz).
Frequency-wavelength—velocity
(See also Resonance.)
The velocity of propagation of a wave is
where f =frequency (hertz) and A= wavelength (metres).
For electromagnetic waves in free space the velocity of propagation vis approximately 3 x JO" m/sec, and if Jis expressed
in kilohertz and A in metres
where S = distance in miles and H = height in feet above sea level.
Impedance
The impedance of a circuit comprising inductance, capacitance and resistance in series is
where R =resistance (ohms), w = 2rr x frequency (hertz), L = inductance (henries), and C =capacitance (farads).
Inductance
Single layer coils
where N = number of turns, a = radius of coil in inches, 11 = number of !urns per inch, L =inductance in microhcnrics (f.LH) and I = length of coil in inches.
Calculation of overall inductance with:
Meter conversions
Increasing range of ammeters or milliammeters
Current range of meter can be increased by connecting a shunt resistance across meter terminals. If R"' is the resistance of the meter; R, the value of the shunt resistance and n the number of times it is wished to multiply the scale reading. then
Increasing range of voltmeters
Voltage range of meter can be increased by connecting resistance in series with it. If this series resistance is R, and R, and n as before, then R, = R.., x (n - I).
Negative feedback
Voltage feedback
where A is the original gain of the amplifier section over which feedback is applied (including the output transformer if included) and b is the fraction of the output voltage fed back.
Q
The Q value of an inductance is given by
Reactance
The reactance of an inductor and a capacitor respectively is given
by
Resistance
Calculation of overall resistance with:
Series resistors- R = R 1 + R 2 + ..
Time constant
For a combination of inductance and resistance in series the time constant (i.e. the time required for the current to reach 63o/c of its final value) is given by
For a combination of capacitance and resistance in series the time constant (i.e. the time required for the voltage across the capacitance to reach 63o/c of its final value) is given by
r = CR seconds
where C =capacitance (farads). and R =resistance (ohms).
Transformer ratios
The ratio of a transformer refers to the ratio of the number of turns in one winding to the number of turns in the other winding. To avoid confusion it is always desirable to state in which sense the ratio is being expressed: e.g. the 'primary-to-secondary' ratio n,Jn,. The turns ratio is related to the impedance ratio thus
where nP = number of primary turns. n, = number of secondary turns. Zp =impedance of primary (ohms). and Z, =impedance of secondary (ohms).
Wattage rating
If resistance and current values arc known.
If wattage rating and value of resistance arc known. the safe current for the resistor can be calculated from
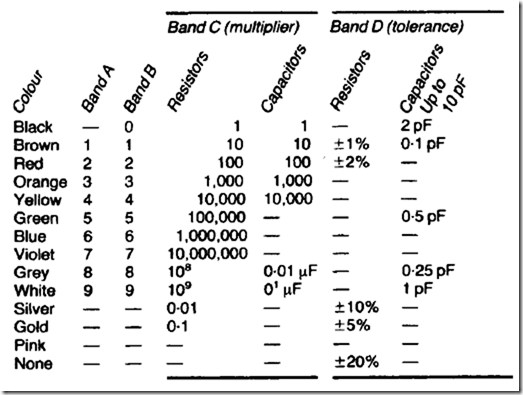
Resistor and capacitor colour coding




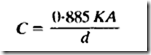
















Comments
Post a Comment