Musical notes frequencies and Radio and electronics glossary.
Musical notes frequencies
The range of notes on a piano keyboard is from 27-5 Hz to 4186Hz. Middle C (the centre note on a standard keyboard) has a frequency of 261-6Hz. Standard pitch is A above middle C at a frequency of 440Hz. Note that raising the pitch of a note is equivalent to doubling the frequency for each complete octave.
Radio and electronics glossary
Absorption coefficient The ratio of the sound energy absorbed by a surface, to the total sound energy incident on it.
Access time Time interval between a received instruction to read data stored in memory and the output of the data from memory.
Accumulator 1 A secondary cell, which produces a potential différence. 2 A register within the central processing unit of a computer.
a.c. Abbreviation for alternating current.
Acoustic feedback Unwanted feedback of sound waves from the output of an acoustic system to its input, causing unpleasant audible oscillations commonly known as howling.
Acoustic wave Synonym for sound wave.
Adder Circuit in a digital computer which performs addition. Address Number that identifies a particular item of data in memory or input/output channel of a digital computer.
Admittance Reciprocal of impedance, symbol Y. The unit of admittance is the Sieme11.
Aerial Construction, usually of metal, which radiates or receives radio waves. Synonym for antenna.
AFC Abbreviation for automatic frequency control. Alphanumeric Alphabetical or numerical ordering.
Alternating current An electric current which periodically changes direction.
AM Abbreviation for amplitude modulation. Ammeter Indicating meter used to measure current. Ampere Unit used to measure current.
Amplify Make larger, electronically.
Amplifier Electronic circuit which increases some aspect of an applied signal.
Amplifier stage A single stage of a complete piece of electronic equipment to amplify an electronic signal.
Amplitude The peak value of an alternating current.
Amplitude modulation Type of modulation in which the amplitude of a carrier signal is varied above and below its nominal amplitude, by an amount proportional to the varying amplitude of a message signal.
Analogue Term used for a non-digital signal. Some part of the analogue signal varies as the analogue of a reference.
Analogue/digital converter A circuit which converts an analogue signal to a digital one.
AND gate Logic circuit whose output is high if all of its inputs are high.
Angular frequency The frequency of a periodic wave in radians s- 1
Symbolw.
Anode Positive electrode of a system. Antenna Aerial.
Antiphase Waveforms completely out of phase, i.e., differing by 180".
Aspect ratio Ratio of the width of a television picture to its height. Typically 4:3.
Assembler Computer program which converts a program written in assembly code to a machine code program.
Astable multivibrator A multivibrator circuit which produces an output of two continuously alternating states, i.e., a square wave oscillator.
Asynchronous U ntimed data transfer.
Attenuation Reduction in some aspect of a signal. Opposite of amplification.
Allenuator A circuit which attenuates an applied input signal. Audio frequency Sound waves within the frequency range of the
human ear, i.e., having a frequency between about 20 to 20,000 Hz.
Automatic frequency control Circuit to control the frequency of an applied signal.
Automatic gain control Circuit to control the amplitude of an applied signal.
Automatic volume control Synonym for automatic gain control. Avalanche breakdown Phenomenon which occurs in a reverse biased semiconductor junction, in which free charge carriers within the junction multiply.
Background noise See Noise.
Balanced A transmission line with two conducting wires, each of which has the same resistance to ground, is said to be balanced.
Band 1 A coloured ring on an electronic component. 2 A specific range of communications frequencies.
Band-pass filter A filter which allows a specific range of frequencies to pass, while attenuating all other frequencies.
Band-stop filter A filter which attenuates a specific range of frequencies, while passing all other frequencies.
Bandwidth The band of frequencies a circu t passes, without the circuit's output amplitude falling by a specified fraction (usually one half) of the maximum amplitude.
Base One of the three terminals of a bipolar transistor. BASIC A high-level computer programming language.
Bass An audio amplifier tone control which attenuates or amplifies bass (i.e. low) frequencies.
Batch processing A computing method used in large computing systems, in which a number of previously prepared programs are run in a single batch.
Battery A source of electricity, consisting of two or more cells connected together.
Baud Unit of data modulation rate, corresponding to one transmitted signalling element per second. Often incorrectly confused with data signalling rate, measured in bits per second.
Beat A periodic signal produced when two signals of similar frequency are combined. The beat is caused by interference: the frequency of the beat is defined by the difference in frequency between the two interfering signals. Synonym for heterodyne.
Bel Unit used to express power ratios in electronics. See Decibel. Beta The common emitter, forward urrent transfer ratio of a transistor. Symbol: {J or h,,.
Bias For a transistor to operate correctly the proper potentials have to be present at its emitter, base and collector. Normally the term
bias refers to the voltage applied to the base to bring the operating '){lint to a linear part of the amplification curve. For germanium transistors this is usually 0·3 V with respect to the emitter and for silicon transistors at least 0·6 V.
Bias voltage A standing voltage applied to an electronic component.
Binary code Numerical representation which has a base of two and, therefore, only two digits: 0 and I.
Bipolar transistor A transistor in which both types of charge carriers (i.e., electrons and holes) are used in operation.
Bistable Abbreviation of bistable multivibrator: a circuit which has two stable states. Commonly known as a flip-flop.
Bit Abbreviation of binary digit. One of the two digits (0 or I) of binary code.
Black box Any self-contained circuit, or part of a system, which may be considered a separate entity. Because of this, a user or circuit designer does not need to understand the black box's internal operation just its effect on external circuits.
Blocking capacitor A capacitor used in a circuit to prevent direct current flow between two parts of the circuit.
Bode diagram A graph in which gain and/or phase shift caused by a circuit, is plotted against frequency of applied signal.
Breadboard A plug-in method of temporarily assembling circuits, for design or test purposes.
Breakdown The sudden change from a high resistance to a low resistance which occurs when the breakdown voltage of a reverse biased semiconductor junction is exceeded.
Bridge A network of components, generally arranged in a square formation.
Bridge rectifier A full-wave rectifier circuit, composed of four diodes in a bridge.
Brightness A surface's brightness is the property by which the surface appears to emit light in the direction of view. This is a subjective quantity.
Broadcast Radio or television transmission.
Bubble memory A type of computer memory device which, although solid-state, is not of semiconductor origin. Data is stored as tiny domains of magnetic polarisation.
Bucket-brigade See Charge coupled device.
Buffer Circuit interfacing two other circuits, used to prevent interference from one to the other.
Bug A comJjuter program fault.
Bus I A conductor between two or more parts of a circuit, generally of high current carrying capacity. 2 A set of conductors between parts of a computer system.
Byte A group of bits, treated as a single unit of data in a computer system. Generally, though not necessarily, a byte is taken to be a group of eight bits.
Cable A set of conductors, insulated from each other but enclosed in a common outer sheath.
Capacitance The property of two isolated conductors whereby they hold an electrical charge. Symbol: C. Unit: F.
Capacitor An electronic component, which has two isolated conductive plates. A capacitor may therefore hold an electrical charge.
Carrier 1 A signal which is modulated by a message signal to allow communications e.g. amplitude modulation. 2 A hole, or electron in a semiconductor device, which carries charge.
Cathode Negative electrode of a system.
Cathode ray A beam of electrons, generated in a cathode ray tube.
Cathode ray oscilloscope An electronic test instrument which allows a signal to be displayed on its screen, as a graph of voltage against time. Abbreviated: CRO.
Cathode ray tube Glass evacuated tube allowing a beam of electrons to be generated, focused and positioned onto its face (screen). Cathode ray tubes form the display device in common TVs and cathode ray oscilloscopes. Abbreviated: CRT.
CCITT Abbreviation for International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee. A body which recommends standards concerning voice and data communications systems.
Ceefax See Teletext.
Cell Device which produces a potential difference by chemical means. Two or more cells in combination form a battery.
Central processing unit The part of a digital computer that controls the computer operation. Abbreviation: CPU.
Channel I A communications path between a transmission source and receiver. 2 The region between the source and drain of a field effect transistor.
Charge carrier A hole or electron in a semiconductor.
Charge coupled device A semiconductor memory device comprising a number of memory cells, each of which may hold a charge. Each charge is passed along from cell to cell, earning the device the nickname bucket-brigade device. Abbreviation: CCD.
Chip I A small piece of semiconductor material containing a single electronic component, or an electronic circuit. A chip is found within every transistor or integrated circuit. 2 Nickname for an integrated circuit.
Clock A circuit or device which generates a periodic signal (generally a square wave) to synchronise operations of a digital system.
CMOS Abbreviation for complementary metal oxide semiconductor.
Coax Abbreviation for coaxial cable.
Coaxial cable A cable with an inner conductor comprising one or more strands of wire, and an outer conduction sheath. The conductors are insulated from each other and the whole arrangement is covered in an outer layer of insulating material.
Coil Conductor (s) wound in a number of turns.
Collector One of the three terminals of a bipolar transistor. Colour code Method of marking an electronic component with
information regarding its value, tolerance and any other aspects
which may be of interest to its user.
Complementary pair Most modern transistor audio amplifiers make use of a pair of transistors, one npn and the other pop, with similar characteristics and closely matched gains in the driver or output stage: they are referred to as a complementary pair.
Computer An automatic system, which processes information according to instructions contained in a stored program.
Conductor A material with low resistance to the flow of electric
current.
CPU Abbreviation for central processing unit. CRO Abbreviation for cathode ray oscilloscope.
Crosstalk Interference between signals of two adjacent communications channels.
CRT Abbreviation for cathode ray tube.
Current Rate of flow of electricity. Symbol:/. Unit: ampere (abbreviated: amp: A).
Cut-off frequency Frequency at which a circuit output falls to a specified fraction (usually one half) of the maximum.
Cycle Complete set of changes in a regularly repeating wave. Darlington pair A combination of two transistors which operate as
if they are a single transistor, with a gain given by the product of the individual transistors gains. dB See decibel.
d.c. Abbreviation for direct current.
d.c. voltage Common term to mean direct voltage.
Debug The action of finding and correcting computer program faults.
Decibel Dimensionless unit expressing the ratio of two powers. Under certain conditions it may also be used to express the ratio of two voltages or currents.
Demodulation See Modulation.
Demodulator A circuit which demodulates a received, modulated signal in a communications system. Synonymous with detector.
Demultiplexer See Multiplexer. Detector See Demodulator.
Device An electronic component or system which contains at least one active element.
Diac Bi-directional voltage breakdown diode; passes current above a certain breakdown voltage. Normally employed with a triac in an a.c. control circuit.
Dielectric A material which is an insulator and can sustain an electric field. The layer of insulating material between the conducting plates of a capacitor is a dielectric.
Dielec:tric constant The ratio of the capacitance of a capacitor with a dielectric, to the capacitance of the capacitor with the dielectric replaced by a vacuum. Synonymous with relative permittivity. Symbol: Jl,. See Permittivity.
Differential amplifier An amplifier which produces an output signal which is a function of the difference between its two inputs. Principle of the operational amplifier.
Differentiator A circuit which produces an output signal which is a function of the differential of its input signal.
Digital A circuit or system responding to, operating on, and producing fixed, discrete voltages. Where only two levels are used, the circuit or system is said to be binary digital.
Digital computer See Computer.
Digital multi meter A multimeter which is capable of measuring and displaying a number of electrical quantities as a decimal value.
Digital voltmeter A voltmeter which displays a measured voltage as a decimal value.
Dl L Abbreviation for dual-in-line.
Diode An active electronic component with two electrodes, which allows current flow in one direction but not in the other. Many derivative types of diode exist.
Diode transistor logic Family of logic integrated circuits built using diodes and transistors. Abbreviation: DTL.
Dioptre The unit of measure of lens power; the reciprocal of the focal length, expressed in metre.
Dipole aerial Simplest type of aerial, in which a standing wave of current is symmetrical about its mid-point.
Dirret current A unidirectional, constant current. Abbreviation: d.c. Dirret voltage A unidirectional, more or less constant voltage.
Distortion Extra unwanted components in the output of a system, which have been added by the system itself. There are many types of distortion.
Doping The addition of impurities to a pure semiconductor material in order to affect the numbers and types of charge carriers present. Donor impurities are added to form an n-type semiconductor. Acceptor impurities are added to form a p-type semiconductor.
Double pole switch A switch with two electrically independent switching mechanisms.
Drain One of the three connections of a field/effect transistor. Drift A variation of an electrical property with time.
Dry battery A battery of two or more dry cells.
Dry cell A cell whose contents are in non-liquid form. Dry joint A faulty soldered joint.
DTL Abbreviation for diode transistor logic.
Dual-in-line Standard package for integrated circuits, in which he connection pins are in two parallel rows, either side of the body.
Duplex Simultaneous operation of both channels of a communications link.
DMM Abbreviation for digital multimeter. DVM Abbreviation for digital voltmeter.
EAROM Abbreviation for electrically alterable read only memory.
Earphone Small loudspeaker which fits into the ear. Earth The arbitrary zero point in electrical potential. Earth current Current which flows to earth.
Earth fault Fault occurring in a circuit or system, when a conductor is connected to earth or a low resistance occurs between the conductor and earth. Causes an unnacceptable earth current.
ECL Abbreviation for emitter coupled logic.
Edge connector A connector which is pushed onto the edge of a printed circuit board. Tracks on the printed circuit board are taken to the edge forming connections.
EEROM, E2 ROM Abbreviation for electrically erasable read only memory.
EHT Abbreviation for extra high tension.
Electrically alterable read only memory See Read only memory. Abbreviation: EAROM.
Electrically erasable read only memory See Read only memory. Abbreviation: EEROM; E2 ROM.
Electrode Part of a component or system which gives out or takes in charge carriers.
Electrolysis Chemical change caused by an applied current through an electrolyte.
Electrolyte material which allows conduction due to its dissociation into ions.
Electrolytic capacitor A capacitor in which the dielectric is formed by electrolytic action.
Electromagnet A component which becomes a magnet only when a current flows through it.
Electromagnetic spectrum Complete frequency range of electromagnetic energy.
Electromotive force Potential difference produced by an electrical energ} source. Abbreviation: EMF. Symbol: E. Unit: volt.
Electron Atomic particle which possesses a negative charge, of magnitude 1.602 x to-· coulomb and a mass of9·109 x w-' kg.
Movement of electrons in one direction is equal to current flow in the opposite direction.
Electron beam Beam of electrons given ofT from an electron gun, typically in a cathode ray tube. Synonymous with cathode ray.
Electron gun Arrangement which is used to generate an electron beam in a cathode ray tube or similar.
Electronvolt The energy gained by one electron when passing across a potential difference of one volt. Symbol: eV.
Element Substance consisting of atoms of only one type. EMF Abbreviation for electromotive force.
Emitter One of the three terminals of a bipolar transistor.
Emitter follower A single transistor amplifier whose output is between emitter and earth.
Enable Activate a circuit or device.
Encoder Circuit, system, or device producing an output which is a coded version of the input.
Energy bands Theoretical levels of energy which electrons of an atom possess.
Equalisation Process whereby the distortion produced by a system may be compensated for.
Equaliser Circuit or device which causes equalisation.
Equivalent circuit A circuit comprising simple (generally passive) elements, used to model the action of a complex circuit under specified conditions.
Erase Remove stored information.
Error Difference between the correct value of something and its actual value.
Exclusive OR gate Logic circuit with two or more inputs, whose output is high if and only if one input is high. Abbreviation: XOR.
Facsimile A picture transmission system by which pictorial images can be transmitted using an ordinary communications link. Abbreviation: fax.
Failure Ceasing of a component or system's ability to function correctly.
Failure rate The number of failures which may be assumed by a component or system, in a given time. The failure rate is given by:
where MTBF is the mean time between failures.
Fall-time The time taken by a logic device or circuit to change output state from high to low.
Fan-out The maximum number of circuits which may be driven by the output of a similar circuit.
Farad Unit of capacitance. Symbol: F.
Feedback The return of some part of a circuit or system's output, to its input in such a way as to control the function of the circuit or system.
FET (field effect transistor) The f.e.t. makes use of the electric field established in a p- or n-type channel of semiconductor material to control the flow of current through the channel. The field is established by the bias applied to the gate connections and the f.e.t. is thus a voltage-controlled device. This means that it has a much higher input impedance than ordinary transistors. The main connections are the source, drain and gate but some f.e.t.s have additional connections.
Fibre optics See Optical fibre.
Field 1 Region affected by some phenomena. 2 Set of bits forming a unit of data with a specific purpose. 3 Set oflines of a displayed television picture.
Field effect transistor A unipolar transistor (i.e. with only one p-n junction). Abbreviation: FET.
Filter Circuit which passes some applied frequencies of signals while restricting others.
Fleming's left-hand rule When the thumb, first finger and middle finger of the left hand are held naturally at right angles, the thumb represents the direction of motion, the first finger represents the magnetic field, and the middle finger represents the current, I,in an electric motor.
Fleming's right-hand rule Similar to Fleming's left-hand rule, but representing a dynamo, with the right-hand.
Flicker The eye's perception of fluctuations of brightness when the fluctuations occur more rapidly than the persistance of vision.
Flicker noise See Noise.
Flip-flop Nickname for a bistable multivibrator.
Floating Term describing a part of a circuit which is not connected. Floating-point representation Means of expressing a number with
the use of a mantissa and an exponent.
Floppy disk Magnetic memory medium used by computers as auxiliary memory.
FM Abbreviation for frequency modulation.
Forward bias When a voltage is applied across a semiconductor junction, the junction is said to be forward biased when the current through the junction is the greater of the two ways. Thus, a diode is forward biased when it conducts and reverse biased when it does not conduct.
Frame One complete television picture.
Frequency Number of complete oscillations or cycles of a periodic signal in one second. Unit: hertz (Hz). Frequency is related to the wavelength (A) of the signal by the signal velocity (v), where
Frequency division multiplex A system in which a number of message signals are combined into one. Each message signal is modulated onto a different carrier wave frequency so that a number of frequency band channels exist. Abbreviation: FDM.
Frequency modulation Type of modulation in which the carrier frequency is varied up and down by the message signal. The carrier amplitude remains constant. Abbreviation: FM.
Frequency range Range of frequencies a circuit will operate on. Frequency response Variation with frequency of the gain of a circuit.
Drawn as a graph, usually of gain in decibels against a logarithmic scale of frequency.
Frequency spectrum A graph, chart, or table showing the frequencies of all electromagnetic waves, related to types, e.g., X-rays, radio waves, audio waves, etc.
FSD Abbreviation for full scale deflection.
Full scale deflection Maximum value displayed by measuring equipment. Abbreviation: FSD.
Full wave rectifier A circuit which rectifies both positive and negative half cycles of an applied a.c. wave.
Function generator A circuit or piece of test equipment which generates a variety Of waves e.g. sine, sawtooth, square, for usc in testing other circuits.
Fundamental frequency Generally the lowest sine wave frequency present in a complex periodic waveform.
Fuse Device which is intended to cause an open circuit when the current taken by a circuit goes above a specified level. Generally, a fuse is formed using a short length of fuse-wire which, at a specified frequency and voltage, will melt, i.e., 'blow' at the fuse's current rating, thus breaking the power supply connection.
Fusible link memory Type of read only memory device consisting of a matrix of fusible links. Data may be programmed into the device by 'blowing' selected links.
Gain Measure of a circuit's effect on the amplitude of an applied signal. Can be stated in terms of the ratio between output and input signals as a decimal number, or in decibels.
Gain control A control which may be used to vary the gain of a circuit.
Ganged Term used to describe variable components which are mechanically coupled so that they all vary simultaneously when a single control is varied.
Gate I A circuit having two or more inputs and one or more outputs. The output(s) varies as a direct result of the states of the inputs. 2 One of the terminals of a field effect transistor.
Gating signal A signal which, when applied to a gate is used to control the gate's output such as the output may be on (and produce an output signal which is some function of another input) or off (producing no output).
Geostationary orbit A satellite orbit in which the satellite lies about 36,000 km above the earth's equatorial plane, such that the satellite appears stationary to an observer on earth.
Geosy orbit Similar to a geostationary orbit, but the satellite traces a figure-of-eight orbit thus appearing to move up and down in one-day cycles to an observer on earth.
Germuiam Semiconductor element used in the majority of early transistors and diodes.
Giga- Unit prefix which means a multiplication factor of 1012 Abbreviation: G.
Grapllics Display of graphical symbols and scenes, generated by a computer.
GI'OIInd Synonym for earth. Abbreviation: Gnd.
Guanl bud Range of frequencies between two ranges of transmission frequencies, left unoccupied to minimise interference.
Half-adder Elementary digital circuit composed of logic gates. See
Adder.
Half-duplex A pair of transmission channels over which two-way communications may take place, although only one channel is operational at any one time, is said to allow half-duplex communications.
Half wave rectifier A circuit which rectifies only one half of each cycle of an applied a.c. wave.
Hall effect An electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs when a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, the direction of which is perpendicular to the directions of both the current and its own magnetic field.
Ham Colloquial term denoting an amateur radio transmitting/receiving enthusiast.
Hardware Physical parts of a computer system, e.g. printer, keyboard, VDU, etc.
Harmonic A signal present in a complex periodic waveform, which is a multiple of the fundamental frequency. The second harmonic is three times etc.
Head Transducer of a magnetic recording system which allows electrical signals to be changed into a magnetic field to write data onto the medium, or converts magnetic data into electrical signals.
Headset Pair of earphones.
Heatsink Metal attachment mechanically connected to a heat producing element in a circuit (e.g. a power transistor) to ensure heat is dissipated away from the element, preventing damage by excessive heat.
Henry Unit of magnetic inductance. Symbol: H.
Hertz Unit of frequency. Equivalent to one cycle of a periodic wave which occurs in one second. Symbol: Hz.
Heterodyne Production of beats by combination of two signals which interfere. Used in a superheterodyne radio receiver to produce an intermediate frequency.
HF Abbreviation for high frequency.
h,, and h 11. See Beta.
Hili Acronym for high fidelity.
High fidelity Commonly used term denoting audio reproduction equipment of good quality.
High frequency Bands of radio transmissions around 10 MHz. Abbreviation: HF.
High level programming language A computer programming language which is more like human language or mathematical notation than the machine code used by the central processing unit of the computer.
High logic level Term denoting a logic I level (in positive logic). High pass filter A filter which allows signal frequencies above a
specific corner frequency to pass without attenuation. Signal frequencies below the corner frequencies are attenuated.
High tension Voltages in the range between about 50 V to 250 Y. Abbreviation: HT.
Holding current The value of current which must be maintained to hold a thyristor in its on state. If the current through the thyristor falls below the holding current, the thyristor turns off and ceases conduction.
Hole An empty space in a semiconductor material due to a 'missing' electron. As electrons are negatively charged, holes are positive. Holes, like electrons, may be thought of as charge carriers, moving through the semiconductor material thus forming a current.
Hole current The current through a semiconductor due to the movement of holes under an applied voltage.
Howl Colloquial term for the sound caused by acoustic feedback.
HT Abbreviation for high tension.
Hum Capacitive or magnetic interference between a mains powered device such as a power supply, and local equipment such as an amplifier. Often heard in audio frequency systems as a low drone of mains supply frequency, or a harmonic of that frequency.
Hunting A system's oscillation about its desired point, caused by
over-correction.
Hybrid integrated circuit An integrated circuit comprising a number of discrete components attached to a substrate and interconnected
to form a circuit. See Integrated circuit.
Hybrid-rr A type of equivalent circuit used to show transistor operation.
Hysteresis Phenomenon occurring in some circuits or systems, in which the output lags behind a changing input. A hysteresis loop is formed a graph of output against input which shows that the value of output depends on whether the input is increasing or decreasing in value.
Hz Abbreviation for hertz.
IC Abbreviation for integrated circuit.
IEC Abbreviation for International Electrotechnical Commission.
lEE Abbreviation for Institute of Electrical Engineers.
IEEE Abbreviation for Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers Inc.
IF Abbreviation for intermediate frequency.
IGFET Abbreviation for insulated gate field effect transistor.
12 L Abbreviation for integrated injection logic.
Illuminance Luminous flux perpendicularly reaching a surface per unit area. The unit of illuminance is the lumen m- 2 or lux.
Image frequency Unwanted input frequency to a radio, causing a spurious output. Synonym for second channel frequency.
Image interference Interference caused by an image frequency.
Impedance The opposition of a circuit to alternating current flow.
Impedance matching The matching of impedances between two circuits, to ensure maximum transfer of power from one circuit to the other.
Impulse noise Noise in an electronic system caused by a single disturbance. See Noise.
Impulse voltage A single, rapidly occurring, pulse of voltage. Impulses are generally unwanted, as they tend to cause impulse noise throughout the system.
Impurities Atoms in a semiconductor material, not of the semiconductor element itself. Impurities may occur naturally or may be deliberately introduced. See Doping.
Incandescence When a material gives off visible light due to its high temperature.
Incandescent lamp Lamp which emits light when its filament is heated by an electric current. The filament often reaches temperatures of 2,50(J'"C and over.
Index error An error occurring in a measuring instrument such that when no measurand is present (i.e., with zero input) a non-zero reading is obtained. Synonymous with zero error.
Indirect wave Radio wave which is reflected by the ionosphere, i.e., it does not travel directly from transmitter to receiver.
Induce To cause a change in electrical or magnetic conditions in a system, by changing the electrical or magnetic conditions of another, local, system.
Inductance A constant occurring when a circuit is magnetically linked with the current flowing through it. Unit: henry.
Induction Abbreviation of electromagnetic induction or electrostatic induction.
Inductor A component which has inductance. Generally, inductors are constructed of some form of coil.
Information technology The study of the combined effects of electronics, computing and communications. Abbreviation: IT.
Infrared radiation Invisible electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths of about 730 nm to about 1 mm.
Inject To introduce charge carriers into a semiconductor junction
area.
Input 1 The signal applied to a system. 2 The terminal at which the input signal is applied.
Input impedance The impedance which a circuit presents to an input signal.
Input/output Term applying to operations performed by, or devices connected to a computer, which allow the computer to receive and send out data. Abbreviation: 1/0.
Instantaneous value The value of any measurand which varied with
time, e.g., instantaneous voltage, instantaneous current.
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc A standardisation body in the USA. Abbreviated: IEEE.
Institute of Electrical Engineers A UK standardisation body. Abbreviation: lEE.
Instruction set The complete list of operations which may be performed by the central processing unit of a computer.
Insulate To prevent unwanted current flow by sheathing a conductor with non-conductive material.
Insulated gate field effect transistor Type of construction of field effect transistor, used in MOSFETs. Abbreviation: IGFET.
Insulator A non-conductor. A material with a very high resistance to flow of electric current. Current flow is assumed to be negligible.
Integrated circuit A device which contains a complete circuit. One of two main methods are used in manufacture. A hybrid integrated circuit is manufactured from discrete components, attached to a substrate and interconnected by layers of metallization. A monolithic integrated circuit is made by building up all components within the circuit onto a single chip of silicon. In recent usage, integrated circuit, chip, microchip, have all become synonymous. Abbreviation: IC.
Integrated injection logic A type of monolithic integrated circuit construction. Abbreviation: 12 L.
Integrator Circuit which performs the equivalent of a mathematical integration on an applied input signal.
Intelligent Any system with processing and storage capabilities, whose actions may be controlled by stored instructions, is said to be intelligent.
lntelsat Acronym of International Telecommunications Satellite Consortium.
Intensity Denoting magnetic or electric field strength.
Interactive Term used to denote computer operation where user and computer communicate in a continuous manner. Generally refers to an on-line situation.
Interference A disturbance to any signal in a system, causing additional, unwanted signals. Interference may be natural or man made. See Hum, Crosstalk, Image frequency.
Interlaced scanning Scanning method used in a television system in which lines are scanned in two separate scans, even lines and odd lines.
Intermediate frequency Signal generated in a heterodyne-based radio receiver, where the received radio signal is combined with a local oscillation signal. Abbreviation: IF. See Heterodyne, Beats.
Internal resistance The small resistance inherent in any source of electricity. The internal resistance limits the voltage which may be produced by the electricity source under load conditions.
International Electrotechnical Commission An international standardisation body. Abbreviation: IEC.
International Radio Consultative Committee An international standardisation committee: part of the International Telecommunications Union. Abbreviation: CCJR.
International Telecommunications Union An international standardisation body. Abbreviation: ITU.
International Telegraph and Telephone Consultative Committee An international standardisation committee: part of the International Telecommunications Union. Abbreviation: CCJTT.
Inversion The production of an opposite polarity in a semiconductor device, due to an applied electric field.
Inverter I A circuit which produces an output which is the inverse of an applied input signal. A digital inverter produces an output which is the opposite logic state to that of the input. 2 A circuit which converts a direct current to an alternating current.
1/0 Abbreviation for input/output.
Jon A particle of material (an atom, molecule, group of atoms, or group of molecules) with an electric charge. Negative ions are called anions: positive ions are called cations.
ISO Abbreviation for International Standards Organisation. Isolate To disconnect two parts of a system, ensuring that no electrical connection exists.
ITU Abbreviation for International Telecommunications Union. Jack A connector pair (plug and socket) allowing quick and easy input or output connections, to or from a circuit or system. Many sizes and types are available.
Jam To cause interference in radio-type transmissions, rendering correct reception impossible.
JEDEC Abbreviation for Joint Electron Device Engineering Council.
JFET Abbreviation for junction field effect transistor. JK Hip flop A type of flip-flop circuit.
Johnson noise A type of noise generated by the random movement
of electrons in resistive components, due to thermal activity. Synonymous with thermal noise.
Josephson junction The junction between a thin layer of insulating material and a superconducting material. A superconducting current can flow across the junction even without an applied voltage.
JUGFET Abbreviation for junction field effect transistor. Junction I The boundary between two layers of material in an electronic device. 2 An electrical connection.
Junctio'l box An enclosed container, in which wires or leads from circuits may be joined, by screw terminals or other means.
Junction capacitance Capacitance between pn junctions in a semiconductor device. Also called barrier, depletion layer or transition capacitances. See Neutralisation.
Junction Held effect transistor A type of field effect transistor. Abbreviation: JFET; JUGFET.
Junction transistor Abbreviation for bipolar junction transistor. Keyboard Part of a computer, with a typewriter-style appearance,
allowing input of instructions and data to the computer.
Kilo- I A prefix denoting a multiple of 103 Abbreviation: k. 2 A prefix to a computing term, denoting a multiple of210 i.e., 1024.
Abbreviation: K.
Kirchhoff's laws Two basic laws of electricity. The first states that: the algebraic sum of all currents into and out of a point in a circuit is zero. The second states that: the algebraic sum of the products of current and resistance in each part of circuit is equal to the algebraic sum of the voltages.
Klystron An electron gun device, used as an amplifier or oscillator at high radio frequencies.
Lag The delay between one waveform and another, measured in time or as an angle. See Lead.
Lamination Thin sheet material, used to make the laminated core of a wound component, e.g., a transformer, a relay.
Land A contact on a printed circuit board. Language Short for programming language.
Large scale integration A level of integration used in the manufacture of integrated circuits. Abbreviated: LSI.
Laser An acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. A laser device is a source of coherent, monochromatic light. The light may not be visible but may be of ultra-violet or infra red origin.
Latch Common name for a bistable multivibrator or flip-flop. LCD Abbreviation for liquid crystal display.
LC network A tuned circuit containing inductance and capacitance.
Lead I The amount by which one waveform is in front of another, measured as a time interval or as an angle. See Lag. 2 An electrical conductor, used to make an electrical connection between two parts of a circuit or system.
Lead-acid cell A secondary cell or accumulator comprising lead metal cathodes and lead dioxide anodes, with a dilute sulphuric acid electrolyte. Lead-acid batteries, formed by a number of series connected cells are commonly used in cars.
Leading edge The portion of a pulse which signals the commencement of the pulse.
Leakage Current flow through a circuit or component due to faulty insulation.
Leakage current That current which flows due to leakage.
Leclanche cell A primary cell comprising a carbon-rod anode and a zinc cathode, with an ammonium chloride solution electrolyte. Leclanche cells with a paste-based ammonium chloride electrolyte are said to be dry and form the basis of many available cells used in common battery-powered appliances.
LED Abbreviation for light emitting diode. Left-hand rule See Fleming's rules.
LF Abbreviation for low frequency.
Light emitting diode A semiconductor diode which emits light as the result of an electroluminescent effect. As electron and hole combine near the junction of the diode, sufficient energy is released to form light. The emitted light is of a particular frequency and so of a particular colour. Light emitting diodes of red, yellow, orange, green and blue are available, as well as infra-red varieties. Abbreviation: LED.
Light-pen A device used with a computer to produce data on a cathode ray tube screen by writing on the screen in a similar manner to writing with a conventional pen on paper. The computer locates the light-pen's position on the screen and produces an image at that point. As the light-pen is moved across the screen many images combine to form, say, a line.
Light sensitive devices Light and heat both affect the conductivity of a pnjunction. Devices are available in which a pnjunction is exposed to light so as to make use of this property. Light falling on the junction liberates current carriers and allows the device to conduct.
Linear Any circuit or system which produces an output directly proportional to the input at any time, is said to be a linear circuit or system.
Lines The physical paths followed by the electron beam of a television receiver's cathode ray tube across the screen. Standard UK television pictures are composed of 625 lines.
Line of flux Imaginary line in a magnetic field. The direction at any point along a line of flux is that of the magnetic flux density.
Line of force Imaginary line in an electric field, the direction of which at any point represents the field's direction at the point.
Liquid crystal display A display comprising a thin layer of liquid crystal material between two electrodes. Application of a potential difference across the electrodes causes the liquid crystal material to change in respect of light transmission. Abbreviation: LCD.
Load I A circuit or system which absorbs power from any other circuit or system. 2 The output power provided by a circuit or system.
Load characteristic A characteristic curve, typically for a transistor, in which the relationship between variables is plotted.
Load impedance The impedance presented to a circuit or system by its load.
Load line A line drawn on the load characteristics of a component which shows the relationship between voltage and current in the circuit.
Local oscillator An oscillator within a radio receiver operating on the superheterodyne principle.
Logic circuit A circuit which performs a logical operation such as AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, EXOR.
Logic diagram A diagram showing the logic elements of a logic circuit.
Logic symbol Graphical symbol representing a logic element.
Long-tailed pair A circuit containing two transistors coupled together so that their emitters are joined with a common emitter bias resistor which provides a constant current. The long-tailed pair
forms the basis of a differential amplifier.
Long wave A radio frequency wave with a wavelength between about I to 10 km.
Loss A dissipation of power due to the resistance of current flow.
Lossless A circuit or system which theoretically loses no power due to resistance.
Lossy A circuit or system which loses a great deal of power due to resistance.
Loudness Subjective measure of sound intensity. Although dependent on intensity it also varies with frequency and timbre of the sound.
Loudness level A comparison of a sound's loudness with a standard sound loudness. The standard sound is a sinusoidal note which has a frequency of 1,000 Hz. The unit of loudness level is the phon.
Loudspeaker A transducer which converts electrical energy into sound energy. Typically, loudspeakers are electromagnetic devices which rely on the applied electrical signal to move a coil of wire in a magnetic field. Attached to the coil is a cone of material which thus also moves with the electrical signal. The cone causes a movement of air, which the ear detects as sound.
Low frequency Radio signals in the frequency band of 30kHz to 300 kHz, having wavelengths between I and 10 km. Abbreviation: LF.
Low level programming language A computer programming language which comprises instructions to the computer in machine code, i.e., binary codes which the computer can directly understand.
Low logic level Term denoting a logic 0 level (in positive logic). Low-pass filter A filter which allows signal frequencies below a specific corner frequency to pass without attenuation. Signal frequencies above this corner frequency are attenuated.
LSI Abbreviation for large scale integration. See Integrated circuit. Luminance A surface's luminance is the objective measure of the light emitted per unit projected area of surface, the plane of projection being perpendicular to the direction of view. The unit of luminance is the candela m 1 Luminous intensity The unit of luminous intensity is the candela (cd).
Machine code The binary codes understood by the central processing unit of a computer.
Magnet Term applied to a substance which generates a magnetic field. A magnet can be temporary or permanent.
Magnetic bubble memory See Bubble memory. Magnetic circuit A closed path of lines of magnetic flux.
Magnetic field Space surrounding a magnet which contains a magnetic flux. A magnetic field may be represented by lines of force.
Magnetic field strength Magnetising force. Symbol: H. Unit: ampere per metre (A m 1 ).
Magnetic flux The flux through an area in the space surrounding a magnet. Symbol: <ll. Unit: weber.
Magnetic flux density Magnetic induction. The magnetic analogue of the electric field. Symbol: B. Unit: tesla (T), or weber per square metre(wm 2 ).
Magnetism The collection of properties exhibited by a magnet or magnets.
Mains Domestic electricity supply distributed through the National Grid system. A voltage of 240 VAC, at a frequency of 50 Hz is obtained from all domestic outlets.
Mains lmm See Hum.
Make To close a circuit by means of a switch or similar component make and break: a type of switch which is automatically opened and closed, thus making and breaking the circuit, by the circuit which it forms part of.
Man-made noise See Noise.
Mark ace ratio The ratio between a pulse's duration and the time between successive pulses.
Maser An acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. Similar to laser except radiations are part of the microwave frequency band, not light.
Mask Photographic reproduction of the circuit to be integrated into an integrated circuit chip by photographic or other means.
Matched termination A load attached to a circuit or system such that it absorbs all the power available from the circuit or system.
Mean life The mean time to failure of a component, circuit or system.
Measurand The quantity to be measured by measuring equipment. Medium frequency Radio signals in the frequency band of 300 kHz
to 3 MHz, having wavelengths between 100m to I km. Abbreviation: MF.
Medium wave A radio frequency wave with a wavelength placing it in the medium frequency band.
Mega- I A prefix to a number, denoting a multiple of 106• 2 A prefix used in computing, to denote a multiple of220 (i.e., 1,048,576). Symbol: M.
Megger A portable insulation testing equipment.
Memory Any device associated with a digital circuit (particularly a computer) which is capable of storing information in digital form. Synonymous with store.
Memory location A storage element with a unique address. Meter Any measuring equipment.
Meter movement The part of an analogue meter which indicates the measured value, typically constructed of a finely balanced moving coil in a magnetic field. The coil rotates when a current flows through it, the amount of rotation is proportional to the value of current.
Meter resistance The internal resistance of a meter. MF Abbreviation for medium frequency.
Micro- A prefix, denoting a multiple of 10 6• Symbol: fl.
Microcomputer I A single integrated circuit which contains all the parts which can be combined to function as a computer, i.e., central processing unit, memory, timing and control circuits. 2 A computer which comprises an integrated circuit microprocessor. 3 A home computer.
Microphone A transducer which converts sound energy into electrical energy.
Microprocessor An integrated circuit which contains the central processing unit of a computer.
Microwave An electromagnetic wave with a frequency between infra-red and radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum. Microwave wavelengths range from about 3 mm to I·3 m.
Mike Abbreviation for microphone.
Milli- A prefix, denoting a multiple of w- 3• Symbol: m.
Mismatch When a circuit's load does not have the same impedance as the load itself.
Mixer I An audio circuit to combine two or more signals. The output signal is merely the addition of the input signals. 2 A radio circuit which combines two or more signals to produce an output signal of a different frequency to the inputs.
Modem Acronym for modulator-demodulator. Any appliance which converts signals from one circuit or system to signals of another circuit or system. Typically modems are used to connect two computers via telephone circuits.
Modulation The alteration of a signal's parameter by another parameter. For instance, a carrier wave's amplitude may be modulated by a music signal. Other parameters which may be modulated include: phase, frequency, or a combination of more than one.
Monochromatic light Light of a single colour, i.e., it has only one frequency.
Monochrome television Black and white television.
Monostable multivibrator A circuit which has one stable state. On application of a triggering pulse, the output of the monostable multi vibrator assumes a second state for a defined period of time,
after which it returns to the stable state. Synonymous with one-shot.
Morse code Internationally agreed code for the transmission of alphanumeric symbols, in which each symbol is transmitted as a combination of short and long pulses (dots and dashes).
Morse telegraphy Electric telegraphy transmitting alphanumeric symbols as Morse code.
MOSFET Abbreviation of metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor. A type of field effect semiconductor.
MOST Type off.e.t. with oxide insulating layer between the metal gate and semiconductor channel. It has a higher input impedance than the junction type f.e.t.
Motorboating Term used to describe an oscillation arising in low or audio frequency amplifiers, resembling a motorboat engine.
Moving coil A device which relies on its motion due to current through a coil in a magnetic field.
Multiplex Combination of two or more signals, such that a single signal is obtained which may be transmitted and later demultiplexed back into the original signals.
Multiplexer A circuit which allows the multiplex process to take place.
Multivibrator A circuit which contains two inverters coupled so that the output of one forms the input of the other. Resistive coupling of the two inverters produces a bistable multivibrator, or flip-flop. Resistive/capacitive coupling produces a monostable multi vibrator. Capacitive coupling produces an astable multi vibrator.
NAND gate Logic circuit whose output is high if one or more of its inputs are low, and low if all its inputs are high.
Nano- A prefix denoting a multiple of w-•. Symbol: n.
Natural frequency The frequency at which free oscillation occurs in a resonant electrical, electronic, or mechanical system.
N hannel The conducting channel of a field-effect transistor of N type semiconductor material. The term is also used to refer to the transistor, i.e., N-channel field-effect transistor.
Negative bias A voltage applied to an electrode of some electronic component, which is negative with respect to a fixed reference potential.
Negative feedback Type of control procedure in which all or some part of a system's output signal is fed back to the system's input terminal. Generally, by changing the amount of negative feedback the system's gain is changed. The gain may thus be controlled by choosing the required amount of negative feedback.
Negative modulation Type of modulation procedure followed in the transmission of television signals, such that a black display results from a more positive signal and a white display results from a negative signal. This principle is followed to ensure that any noise which a television receiver picks up produces a darker image and is thus less noticeable than it would be if positive modulation were used.
Neon indicator Type of indicator, relying on the gas-discharge properties of the inert gas, neon. A voltage of about 80 V is required to illuminate such indicators, and so they are typically used as indicators to display the presence of mains voltages.
Neper A dimensionless unit used to express the ratio of two signal powers. One neper equals 8·686 decibels .. Symbol: Np.
Network Alternative term describing a circuit.
Neutral l One of the three lines of the domestic mains electric supply. 2 Descriptive term implying no overall positive or negative charge.
Neutralisation In radio frequency transistors there is a tendency for self-oscillation to occur due to the collector-base capacitance. In modern r.f. transistors this capacitance can be made very small. To overcome the effect in early r.f. transistors it was usual to use a small amount of capacitive negative feedback in each stage, this being known as neutralisation.
Nicad Abbreviation for nickel cadmium.
Nickel admium cell A secondary cell, with a nickel-based anode, a cadmium cathode and a potassium hydroxide electrolyte. Abbreviation: nicad cell.
Node Any point on a transmission line, where standing wave is of zero value.
Noise Unwanted signals occurring in a electronic system, causing spurious output signals. Noise can be the result of man-made causes, or natural causes. Many different types of noise exist, named after their basic nature, e.g., thermal noise, atmospheric noise, white noise, impulse noise.
Noise factor The ratio of a device's or circuit's input signal-to-noise, to its output signal-to-noise. Synonymous with noise figure.
Noise figure See Noise factor.
Non-linear Any circuit or system which produces an output which is not directly proportional to its input at all times is said to be non linear.
Nonvolatile memory Type of memory in which data is maintained even when power is disconnected.
NOR gate Logic circuit whose output is high if all the inputs are low. If one or more inputs are high, the output is low.
NOT gate Logic circuit whose output is always the inverse of the input. Synonymous with inverter.
NPN transistor A bipolar transistor formed by three layers of semiconductor material the outside two layers being of N-type material, the middle layer of P-type material.
NTSC Abbreviation for National Television System Committee. An American committee, responsible for television standards. The initials NSTC are often comically described as never the same colour referring to the constant colour changes inherent in the system.
N-type semiconductor Semiconductor material containing a higher concentration of negative charge carriers, i.e., electrons, than positive charge carriers, i.e., holes.
Numerical control Type of automatic control system in which a number generated by the controlling device is compared with a number generated by another device. The difference between the two numbers is detected by the controlling device and used to generate a control signal.
Nyquist diagram Graph of a system's performance, which may be used to determine the system's stability under untested criteria.
OCR Abbreviation for optical character reader.
Octave A difference or interval between two sounds, whereby one sound is twice the frequency of the other.
Off-line A computer peripheral which is unconnected to the computer is said to be ofT-line.
Ohm The unit of resistance, reactance and impedance. One ohm is the resistance between two points when a constant current of one amp flows as the result of an applied voltage of volt between the points.
Ohmic A material which follows Ohm's law is said to be ohmic. Ohmmeter An instrument which measures resistance. Ohmmetre The unit of electric resistivity. Symbol: Om.
Ohm's law Law which defines the linear relationship between the voltage applied across a material, the current produced through the material, and the resistance of the material. Ohm's law can be written:
V=IR
One shot Synonym for a monostable multivibrator.
On-line A computer peripheral which is connected to and receiving or transmitting data from or to a computer, is said to be on-line.
Opamp Abbreviation for operational amplifier.
Open circuit Term applying to a circuit or system whose output is not connected to any following circuit or system. The output is therefore unloaded. Measurements of electrical parameters at this time are said to be under open circuit or no lead conditions.
Operating'point The point on a semiconductor device's characteristic curve, representing electrical parameters when defined conditions are applied to the device.
Operational amplifier An amplifier, generally in integrated circuit form, which is usable with only a few components and power supply connections.
Optical character reader A computer input peripheral which is capable of converting symbols printed on paper into digital signals.
Oracle The Independent Broadcasting authority's version of broadcast teletext.
OR gate Logic circuit whose output is high if one or more of its inputs are low.
Oscillation A-periodic variation of an electrical parameter.
Oscillator A circuit or system which produces on oscillation.
Oscilloscope Test equipment which is able to produce a visual display of one or more oscillations of voltage. Generally the device used to display the voltages is a cathode ray tube and such oscilloscopes are often referred to as cathode ray oscilloscopes (shortened to CRO ).
Output I The part of a circuit or system which produces an output signal. 2 The signal produced by a circuit or system.
Output impedance The impedance of the output of a circuit or system.
Overall efficiency The ratio of the power absorbed by a circuit or system to the power supplied by a source.
Overdamping Damping applied to a period oscillation which prevents the oscillation from completing one cycle before stopping.
Overdriven Term, generally applied to a linear system such as an amplifier, which refers to the state when the size of input signal is such that the system's output is non-linearly related. In the case of an overdriven amplifier the output sounds harsh and is known as distorted.
Oxidation A process in the manufacture of semiconductor devices when the semiconductor base material undergoes a reaction with oxygen, to form a semiconductor oxide.
PA Abbreviation for public address system.
PABX Abbreviation for private automatic branch exchange.
Packing density The number of transistors or gates in unit area on an integrated circuit chip.
Pair Two similar conductors, insulated from each other but running in parallel, forming a transmission line. Generally, the pair is in the form of wire, e.g., twisted wire pair, coaxial cable.
PAL Abbreviation for phase alternation by line.
PAM Abbreviation for pulse amplitude modulation.
Parallel Components are said to be in parallel if current from a single source divides and flows through them then later reunites.
Parallel circuit A circuit containing two or more components connected in parallel.
Parallel plate capacitor A capacitor formed from two parallel conductive plates, between which is the dielectric.
Parallel resonant circuit A circuit containing a capacitance in parallel with an inductance, which exhibits resonance.
Parameter A criterion of an electronic component, circuit, or system. Typical parameters are voltage, current, resistance, capacitance, etc.
Parametric amplifier I A microwave frequency amplifier, whose reactance is varied in a regular manner. 2 An audio frequency amplifier which can amplify or attenuate specific frequency signals, while passing other signals unaltered. It is thus a bandpass/band reject filter, whose centre frequency may be adjusted.
Pascal A high level programming language.
Passive Any component which does not introduce gain is known as a passive device.
P-.,hannel The conducting channel of a field-effect transistor of P type material. The term is also used to refer to the transistor, i.e., P channel field-effect transistor.
PCM Abbreviation for pulse code modulation.
PD Abbreviation for potential difference.
Peak-to-peak amplitude The difference between extreme values of a periodic oscillation.
Peak value The extreme value of a periodic oscillation.
Period The time to complete a single cycle of an oscillation. Symbol: T.
Periodic Term used to describe any variable which exhibits a regularly occurring form.
Peripheral devices Devices which connect to a computer.
Permanent memory Non-volatile memory, i.e. memory, the contents of which remain intact without a supply of power.
PFM Abbreviation for pulse frequency modulation.
Phase The amount by which a periodic variable has progressed from a reference point. Phase can be measured as an angle or in radians. Two periodic variables with the same frequency and waveform which reach corresponding stages simultaneously are said to be in phase. Irthis does not occur, they are said to be out of phase.
Phase alternation by Hne A colour television system, variations of which have been adopted throughout Europe, in which the colour signal (known as the chrominance signal) is resolved into two components and transmitted separately. The phase difference of these two components is reversed on alternate lines, a procedure which helps to reduce errors due to received phase variations. Abbreviation: PAL.
Phase difference Difference in phase between two sine waves of the same frequency.
Phase modulation Modulation in which the phase of a carrier wave is varied by an amount proportional to the amplitude of the message signal. Abbreviation: PM.
Phase sbift keyiag Alternative name for simple phase modulation of a digital signal. Abbreviation: PSK.
Photocell A transducer which converts light to some parameter of electricity.
Photodiode A semiconductor diode device, which conducts electric current by an amount proportional to the quantity of light falling on it.
Photoresist Photosensitive material which changes in molecular ways upon exposure to light. Photoresists are used in the manufacture of semiconductors and integrated circuits and printed circuit boards.
Pick-up A transducer which converts recorded signals into electrical signals.
Pico- Prefix denoting a multiple of 10- 12 Symbol: p.
Pletwe element The smallest portion of a graphic or pictorial display system which can be resolved by tbe system. Often shortened to pixel.
Piezoelectric cryshll A crystal which displays the piezoelectric effect.
Piezoelectric effect An effect observed in certain materials when a voltage is generated across the faces of the material as a mechanical stress is applied.
p-i-n clilllle A diode which contains a layer of intrinsic, i.e., pure, semiconductor between the P and N layers.
PM Abbreviation for phase modulation.
PN junction The junction between two layers of semiconductors of P-type and N-type origin.
PNP tramis!Ot" A bipolar transistor formed by three layers of semiconductor materials -the outside two layers being of P-type material, the middle layer ofN-type materiaL
Point contact device One in which the pn junction is formed at the contact between a metal•cats-whisker' and the semiconductor materiaL Point contact diodes have advantages in some applications.
Polarised Term used to describe any component or device which must be inserted into a circuit a particular way round.
Positive feedback Type of control procedure in which part of the output signal of a circuit is fed back to the input terminal in such a way that the circuit regenerates the signal, resulting in greater amounts of signal fed back, resulting in further regenerates. Generally, the result of positive feedback is to form an oscillation.
Pot Abbreviation for potentiometer.
Potential Abbreviation for potential difference. Potential difference The voltage across two points.
Potential divider A circuit consisting of a number of series components. Tapping at one of the junctions between components allows a fraction of the total applied voltage to be obtained. Synonymous with voltage divider.
Potentiometer A form of variable resistor with three contacts. A voltage is applied across the outer two (across the total resistance) and the third contact (the wiper) may be varied along the length of the resistance forming a variable voltage divider. Abbreviation: pot.
Power Rate at which energy is used up or work is done. The electrical unit of power is the watt. Abbreviation: W. Symbol: P.
Power ratio The unit of acoustical or electrical power measurement in comparison with a standard level is the bel. In practical terms, power ratios are usually expressed in decibels (dB).
Power supply A source of electrical power for electronic circuits. Usually the power supply is integral to the equipment. Abbreviation: PSU (for power supply unit).
Power transistor A transistor which operates at high values of power.
PPM Abbreviation for pulse position modulation. Preamp Abbreviation for preamplifier.
Preamplifier Part of an amplifying system which amplifies small applied input signals, generally amplifying in terms of voltage amplitude only.
Preferred values Predetermined component values. Their use makes component manufacture relatively simple, as only a selected few values need be manufactured, not every possible value.
Prestel See Videotex.
Primary ceD A cell whose structure does not allow it to be recharged.
Printed circuit board Method of manufacturing electronic products, in which all or most of the circuit is constructed on a thin board (the printed circuit board). Connections between components are formed with thin strips of copper. Abbreviation: PCB.
Printer Computer peripheral which prints characters or symbols onto paper.
Program The complete set of instructions which can control the operation of a computer.
Programmable read only memory Computer memory which may be programmed, i.e., have data written into it, once. After this it may only be read from. Abbreviation: PROM.
Programming language Any language which may be understood by computers and humans. Computers ultimately require instructions in machine code, so this is the simplest programming language. It can be understood by humans but not easily. Low level programming languages resemble machine code and are thus still difficult in terms of human use. High level programming languages resemble human languages and are thus easier for humans to use.
PROM Abbreviation for programmable read only memory.
P- type semiconductor Semiconductor material containing a higher concentration of positive charge carriers, i.e., holes, than negative charge carriers, i.e., electrons. In effect holes are simply a depletion of electrons, but nevertheless can be viewed as small objects which
carry a charge through a semiconductor.
Public address system Sound reproduction system used to amplify sound and thus allow it to be relayed to many people over a large area. Abbreviation: PA.
Pulse A single variation in voltage or current from a zero value, to a maximum and back to zero.
Pulse amplitude modulation Pulse modulation system in which the amplitude of a pulse is modulated with respect to the amplitude of a message signal. Abbreviation: PAM.
Pulse code modulation Pulse modulation system in which pulses are produced corresponding to the message signal. Abbreviation: PCM.
Pulse modulation Any modulation system in which a train of pulses is used as the carrier. Abbreviation: PM.
Pulse position modulation Pulse modulation system in which the position of each pulse is related to the message signal. Abbreviation: PPM.
Pulse width modulation Pulse modulation system in which the width of each pulse is modulated with respect to the message signal. Abbreviation: PWM.
Push-pull Circuit operation in which two devices operate totally out of phase.
Q-factor Abbreviation for quality factor.
Quadrophonic Referring to a sound reproduction system with four separate sound channels.
Quadrature Two sine waves of the same frequency but 90" out of phase are referred to as being in quadrature.
Quality factor A variable which describes the selectivity of a circuit. It is typically used in conjunction with resonant circuits. The quality factor may be calculated from the expression:
where Q is the quality factor, B is the bandwidth of the circuit, and/ is the centre frequency of the circuit. Abbreviation: Q-factor.
Quantisatiou The production of a number of quantised, i.e. discrete, values which may be used to describe a continuous waveform. The best example of the use of quantisation is in the process of pulse modulation, where the sampled values are used to define some aspect of a pulse train.
Qurtz A type of crystal which exhibits the phenomenon of piezoelectricity.
Qurtz-crystal 08C11lator An oscillator which relies on the principle that crystal will vibrate at a fixed natural frequency.
current Current which flows through any component or part of a circuit under normal conditions, when no signal is applied.
Qtriescent point Point on a semiconductor's characteristic curve representing the parameters of the device when in a quiescent state.
Ra4ar An acronym of radio direction and ranging. A system capable of locating distant objects using reflected radio waves.
Radiation Any form of energy transmitted as electromagnetic waves, or as streams of particles.
Radio The use of electromagnetic radiation within the frequency range of about 3kHz to 300 GHz to transmit information without connecting wires.
R•diowave Any electromagnetic radiation with a frequency within the radio frequency range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz.
RAM Abbreviation for random access memory.
Rudom «ess menMWY Type of computer memory which may be accessed randomly, i.e., directly (non-sequentially).
Raster Term describing the pattern of lines on a television-type display screen, which occurs at all times.
R•lings Specification sheets for transistors cov.er many facets of the device's operation but most parameters are needed only by the designer. The ratings which need to be known for replacement purposes are Vc,.,...,, the maximum collector to emitter voltage; fc the collector current; h,., the gain and f. the cut-off frequency. The output power also needs to be observed. RC Abbreviation for resistor-capacitor.
RC network Abbreviation for resistor-capacitor network. Any circuit or network which consists primarily of a resistor and a capacitor.
Reactuce The part of the total impedance of a circuit, which is due to capacitance or inductance, and not to resistance. Reactance causes the current and voltage to become out of phase (in a circuit of pure resistance, current and voltage are in phase Symbol: X. Unit: ohm.
Racti.-e Ion A load with reactance, which thus causes the applied current and voltage to be out of phase.
Reactor A component with reactance, i.e., a capacitor or inductor.
ReiHl To retrieve information previously stored in a computer-type memory device.
ReiHl oaly _.y A computer-type memory device, from which information can only be read from, and not stored into. The information held in a read only memory is generally stored at the 111anufacture stage and is specific to the operation of the computer. Abbreviation: ROM.
Read-write t-d Device used to record and retrieve information to and from a magnetic memory.
Real time operation Use of a computer during the actual time a process is occurring, to monitor and control the process.
Receiver The part of a communication system which receives encoded information from a transmitter, and decodes it to the form required.
Record Any permanent or semi-permanent storage of electrical information.
Rectifier Any device which passes current in only one direction. A rectifier is thus an a.c.-to-d.c. converter.
Redundancy I The use of extra components in a circuit or system to ensure that breakdown of one component does not affect operation ofthe circuit or system. Redundancy is a method of increasing reliability. 2 Inclusion of extra information in a transmitted signal which may be eliminated without loss of essential information.
Refracti•e index The ratio (n) of the velocity of light in free space to that in the material.
Refresh The restoration of information stored so that the information is not lost, typically in a dynamic memory device, or in devices with a destructive read operation.
Regeneration Synonym for positive feedback.
Register One of the temporary storage locations within the central processor of a computer, used to store the results of operations and calculations performed.
Regulator A circuit or device which maintains a constant output voltage or current, regardless of input voltage or output current requirements.
Rejection band The band of frequencies which are not passed through a filter.
Relative permittivity The ratio of the difference between the permittivity of a capacitor dielectric and the permittivity of free space.
Relaxation oscillator An oscillator which relies for its operation on an increasing and decreasing current or voltage within each period of oscillation.
Relay An electrical component in which an applied voltage or current electromagnetically operates a switching mechanism. The contacts of the switch can be isolated from the electromagnet providing a means whereby separate circuits may be interfaced without the need for electrical contact. Modern relays, although providing the same function, are often of a solid state form.
Reliability The ability of a component, circuit, or system to perform its functions for a given period of time.
Reluctance The magnetic equivalent of resistance.
Repeater A device or circuit which amplifies, regenerates, or restores to its original condition a signal in a telecommunications system, which has deteriorated due to transmission over a distance.
Resistance The ability of a material to resist the How of electric current and to convert electrical energy into heat. A material's resistance is given by the ratio of applied voltage across it to the current How through it caused by this voltage. Symbol: R. Unit: ohm.
Resistivity The ability or a material to have a resistance dependent on the material's cross-sectional area and its length. The resistivity of a material is given by
where pis the resistivity, R is the resistance, A the cross-sectional area, and L the length.
Resistor An electronic component which possesses resistance. A pure resistor possesses only resistance, no capacitance or inductance, but all practical resistors possess some small amount or capacitance or inductance. Usually these are sufficiently small to be negligible.
Resonance Phenomenon arising when a circuit or system is excited by an applied signal, so that a small input signal produces a relatively large output signal, at the system's resonant frequency.
Resonant frequency The frequency at which a resonant circuit naturally resonates. Symbol: w.
Reverberation The persistence of sound inside an enclosure, due to multiple reflections from the inside surfaces or the enclosure.
Reverberation time The time required from the cessation of a sound, for the intensity to fall by 60 dB (that is, one millionth of the original value). The unit or reverberation time is the second.
Reverse bias Voltage applied to a PN junction, such that the P-type layer or semiconductor is negative with respect to the N-type layer. Synonymous with reverse voltage.
Reverse Voltage Synonym for reverse bias. Rewrite Synonym for refresh.
RF Abbreviation for radio frequency.
Rheostat A variable resistor used specifically to alter the current How in a circuit.
Right hand rule See Fleming's right-hand rule.
Ringing The delay which a system exhibits in returning to its quiescent state after a sharp pulse input, due to inherent resonance within the system. Generally a period of oscillation occurs, gradually dying away. Damping the system will reduce this period.
Ripple A small a.c. signal superimposed on a d.c. voltage or current, typically found on the output or a d.c. power supply, where the frequency oft he ripple is mains frequency, i.e., 50 Hz or sometimes twice this frequency.
Rise time The time taken for a pulse's leading edge to rise from 10% to 90% of its final value.
RMS Abbreviation for root mean square. ROM Abbreviation for read only memory.
Root mean square Term used to describe the effective value or an a.c.
waveform. It is the square root oft he mean value or the squares or the instantaneous values or the waveform. In the specific case of a sinewave, the root mean square value is equal to the peak value
divided by ../2. Abbreviation: R MS.
RS flip-flop See Bistable.
Rumble Unwanted noise heard in a hi-fi system, caused by mechanical vibrations in the record playing deck, of low frequency.
Sampling The extraction of portions of an electrical analogue signal, used to produce a series of discrete values.
Satellite Artificial body in orbit around the earth for purposes of communications, either one-way from the satellite to the earth, or two-way from earth to satellite and back.
Saturation When the output current of an electronic device is constant and independent of input.
Sawtooth oscillator A relaxation oscillator which produces a sawtooth shaped waveform.
Scanning Process of controlling the electron beam horizontally across and vertically down the face of a cathode ray tube device.
Schematic Circuit diagram.
Schmitt trigger Bistable circuit in which the binary output is determined by the magnitude of the input signal in such a way that the circuit exhibits hysteresis -the output changes when the input exceeds a predetermined level, and changes back when the input falls below a lower predetermined level.
Scramble Process of rendering a communications signal unintelligible at the receiver unless a descrambling circuit is used.
Screen I Surface of a cathode ray. 2 Shield to prevent electromagnetic interference.
SCS Acronym for silicon controlled switch.
SECAM Acronym for sequential couleur a memoire; a line sequential colour television standard.
Secondary cell Rechargeable cell.
Secondary emission Emission of electrons from a material as the result of a bombardment by high-velocity electrons or positive ions.
Secondary voltage Voltage developed across the secondary windings of a transformer.
Selectivity Ability of a radio receiver to discriminate against carrier frequencies different to that selected.
Semiconductor device Device whose operation is based on the use of semiconductor material. In addition to transistors and diodes there is a wide range of components which make use of semiconductor effects.
Semiconductor material Material whose conductive properties depend on the addition of minute quantities of impurity atoms. Unlike normal conductors, semiconductors increase in conductivity with an increase in temperature.
Sensitivity I The change in output of a device per unit change in input. 2 Ability of a radio receiver to respond to weak input signals.
Sensor Transducer.
Serial transmission Communication method in which characters are transmitted in turn along a single line.
Series Components in series have one current flowing through each.
Shift register Digital store of information, in which the information is displaced one place in either direction on application of a shift pulse.
Short cireuit Unwanted electrical connection between two points in a circuit.
Short wave Radio wave in the wavelength range from 10 to 100 metres.
Shunt Parallel connection.
Siemens Symbol: S. The SJ unit of electrical conductance. Signal Variable electrical parameter.
Signal generator Device which can generate a controlled signal.
Signal-to-noise ratio The ratio of the value of signal at a point in a system, compared with the value of noise at the same point. Usually expressed in decibels.
Si6con Semiconductor element, most widely used element to form semiconductor devices.
Silicon controlled rectifier Abbreviation SCR. Thy ristor.
Simplex Communications channel operating in one direction only. Sinusoidal Waveform identical in shape to a sine function.
Slew rate The rate at which the output of a circuit can be driven from one limit to the other.
Smoothing cireuit Circuit designed to reduce ripple in a direct current or voltage.
Solid state circuit A circuit in which the current flows through solid material instead of through a gas or vacuum.
Super alpha pair See Darlington pair. Synchronous Clocked.
Telecommunications The transfer of information by any electromagnetic means.
Telemetry Measurement at a distance using electromagnetic means. Telephone Communication of speech and/or other sounds via electromagnetic means.
Television Communication of video and audio information by electromagnetic means.
Thermal runaway Semiconductor materials are very sensitive to heat - germanium much more so than silicon. Circuit design has to take account of this and many components have to be included to prevent increased current flow due to heat. Without such protection heat induced current will raise the temperature leading to a further increase in current and so on, a process known as thermal runaway which can destroy a semiconductor. See Heat sink.
Thermionic emission Electron emission from the surface of a body, due to the temperature of the body.
Thermistor A semiconductor whose resistance varies with temperature. Some have a negative temperature coefficient, that is resistance falls with an increase in temperature, others have a positive temperature coefficient. Typical applications are to provide compensation for the effects of heat on circuit operation.
Tbevenin's theorem A theorem used to simplify the analysis of resistance networks.
Threshold of bearing The sound level or intensity which is just audible, for an average listener. For a pure sinusoidal tone of 1,000 Hz, it corresponds approximately to a root mean square pressure of Thyristor Three junction, four layer semiconductor rectifier which conducts when either the voltage across it reaches a breakdown point or when triggered by a pulse at its gate electrode. Once triggered it remains conducting until the voltage across it becomes zero.
Trans duce F Any device that converts one parameter into another, where one of the parameters is an electrical signal Transformer Device which transforms electrical energy at its input to electrical output at its output. Usually the voltages of the electrical energies differ.
Transistor Semiconductor device in which the current Oowing between two electrodes may be modulated by the voltage or current applied to other electrodes.
Triac Bi-directional thyristor.
Tuooel diode A heavily doped semiconductor diode which exhibits a negative-resistance characteristic, i.e. over part of its characteristic increased forward bias leads to a reduction in the current Oowing.
Type numbers The numbers in a transistor designation rarely describe anything about its characteristics. In the 2N series adjacent type numbers are frequently widely differing devices. European and British transistors are frequently coded with the first letter A (germanium) orB (silicon) followed by a second letter which indicates the type:
Ultrasonics Sound frequencies above the limits of human ears, generally classed as above 20 kHz.
Ultraviolet radiation Electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths between visible light and X-rays.
Unijunction transistor Three terminal transistor comprising an n type silicon bar with a base contact at each end (base I and base 2) and a p-type emitter region. Current How from one base to the other is controlled by the emitter current; when the emitter voltage
reaches a certain level the emitter-base I junction virtually short
circuits. With a suitable charging circuit at the emitter the device
operates as a relaxation oscillator.
Valency The ability of atoms to unite with other atoms due to the electrons that exist in the outer orbit, or valency band, being able to form a shared orbit with other atoms.
Varicap diode Varactor. When reverse biased, all pn junctions exhibit capacitance, as the depletion layer at the junction forms an insulator between the conductive regions. This property is used in the varicap, in purposes such as automatic tuning and AFC in radio receivers.
VDU Abbreviation for visual display unit. VHF Abbreviation for very high frequency.
Voltage-dependent reSistor Resistor using semiconductor material whose resistance varies with applied voltage.
Voltage drop Voltage between any two points of a circuit, due to the current flow between them.
Watt Symbol: W. SJ unit of power.
Wave A periodic motion, through a medium (which may be space) in which the propagation from a point is a function of time and/or position.
White noise Noise with a wide, flat frequency response.
Word A string of bits corresponding to a unit of information in a digital circuit.
Wow Low frequency (below 10Hz) periodic variations in the pitch of the sound output of a sound reproduction system.
Write To enter information into a storage element.
Yagi aerial Directional aerial array most television aerials are based on the Yagi aerial.
Zener diode Voltage regulating diode. A pnjunction diode which has a defined reverse breakdown voltage. Once in the breakdown region large increases in current produce negligible variation in the voltage across it.
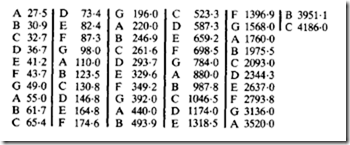



Comments
Post a Comment